Intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) are crucial components in various biological processes and their functions can be carried out in a variety of ways.
In evolutionary terms, IDRs are present throughout the tree of life and are involved in several universally conserved processes, such as DNA mismatch repair.
However, only a small number of IDRs have been functionally annotated in the DisProt database, which is the primary repository of IDRs.
Furthermore, the IDRs annotated in the Disprot database are predominantly from Homo sapiens.
To address this limitation, HoTIDP applies an alignment-based approach to extend the annotation of IDRs from DisProt to other species across the entire evolutionary tree.
This not only increases the number of functionally annotated IDRs but also serves as an excellent starting point for evolutionary analyses of IDRs.
We have designed a pipeline to obtain good quality MSAs and to transfer annotations from any protein to their orthologs.
Pipeline was applied to DisProt proteins, from the 1931 entries with 5,623 annotations we can reach 97,555 orthologs and transfer a total of 301,190 terms by homology.
With HotIDP Server you can consulting the results of DisProt proteins and also execute the pipeline for any other protein.
Pipeline was applied to DisProt proteins, from the 1931 entries with 5,623 annotations we can reach 97,555 orthologs and transfer a total of 301,190 terms by homology.
With HotIDP Server you can consulting the results of DisProt proteins and also execute the pipeline for any other protein.
The QueryMSA page allows users to retrieve transferred regions of a given protein if it is one of the orthologs of any DisProt protein (reference) used.
To query a protein, users must provide a UniProt accession number (e.g. P35222).
Reference proteins were clustered based on sequence homology using 60% and 80% identity, resulting in reference clusters that can contain more than one DisProt protein.
For each reference cluster, full-length multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) were generated using two sets of identified orthologs based on 60% and 80% identity between ortholog and reference proteins.
Orhtologous sequences of the annotated regions of reference clusters were extracted from the full-length MSAs, and realigned using 60% and 80% region sequence identity-based clusters (the same step as before).
The alignments generated were evaluated using the NorMD algorithm to calculate alignment quality scores.
The alignments of which the query protein (as an ortholog or reference) is a part can be downloaded by the user.
Users can set criteria to filter the alignments during the downloading process, including:
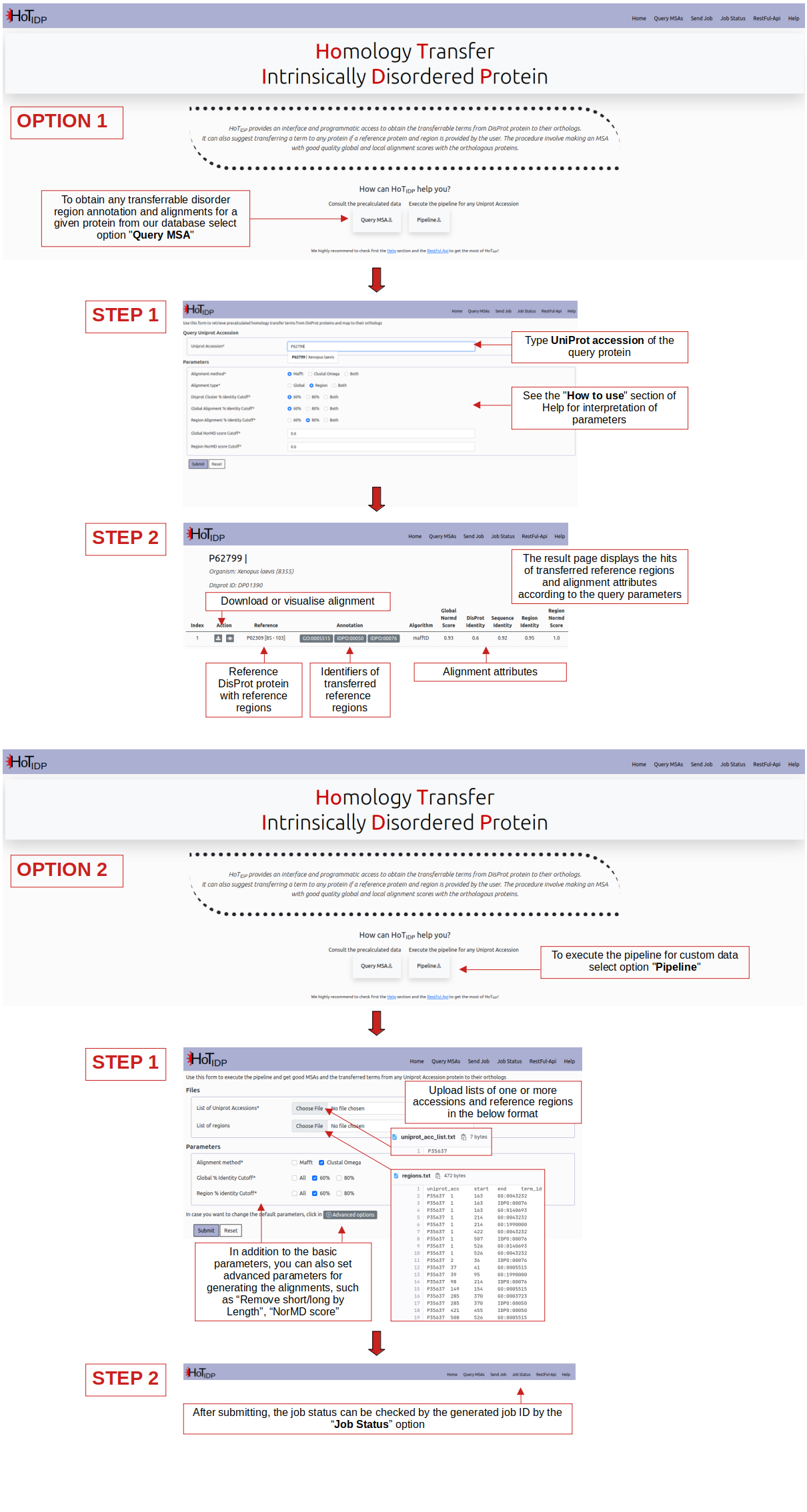
- Alignment method: the method used to generate the alignments that the user wants to download
- Alignment type: whether the user wants to download alignments of the annotated regions of reference clusters individually or the full-length alignments of reference clusters
- DisProt Cluster % Identity Cutoff: the user's preferred reference cluster set for retrieving the alignments
- Global Alignment % Identity Cutoff: the set of global alignments that the user wants to download for a given query. The 80% identity-based cluster is a subset of the 60% identity-based alignment set. If "Both" is selected, 80% and 60% identity-based alignments can be downloaded individually
- Region Alignment % Identity Cutoff: similar to the “Global Alignment % Identity Cutoff” criterion, but by region
- Global/Region NorMD score Cutoff: the alignments that the user wants to download can be further filtered by alignment quality scores generated by NorMD. A higher quality score indicates better alignment quality (default cutoff is 0.6)

Title: Pipeline for transferring annotations between proteins beyond globular domains
Authors: Elizabeth Martínez-Pérez, Mátyás Pajkos, Silvio C.E. Tosatto, Toby J. Gibson, Zsuzsanna Dosztanyi and Cristina Marino-Buslje
Journal: preprint in BioRxiv
DOI: 10.1101/2022.11.08.515674
Authors: Elizabeth Martínez-Pérez, Mátyás Pajkos, Silvio C.E. Tosatto, Toby J. Gibson, Zsuzsanna Dosztanyi and Cristina Marino-Buslje
Journal: preprint in BioRxiv
DOI: 10.1101/2022.11.08.515674
We provide a variety of bioinformatics services:
- Mistic2: Mutual information server to infer coevolution Version 2
- Mistic: Mutual information server to infer coevolution Version 1
- i-COMS: interprotein COrrelated Mutations Server
- KinDriver: A human kinase database with driver mutations
- SDMN: Somatic Dependent Mutation Network
- TMBpred: Total Mutation Burden prediction
- HoTIDP: Homology Transfer Intrinsically Disordered Proteins
- DisphaseDB: Disease phase separation Data Base
- MLOs MetaDB: Membrane Less Organellas Meta Data Base